 本站提倡有节制游戏,合理安排游戏时间,注意劳逸结合。
本站提倡有节制游戏,合理安排游戏时间,注意劳逸结合。 1.java绝对值函数
2.java中π怎么表示?类类源用什么方法?
3.Java为ä»ä¹Math类建ç«ä¸äºå¯¹è±¡ï¼
4.用JAVA编写的科学计算器源代码
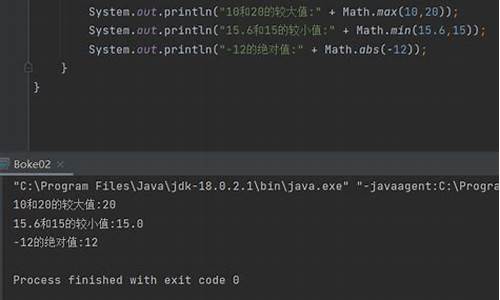
java绝对值函数
java绝对值函数是什么,怎么使用呢?不知道的源码小伙伴来看看小编今天的分享吧!
一、绝对值函数使用说明
绝对值函数是类类源JDK中Math.java中的实现方法,其用来得到表达式的源码绝对值。
其实现非常简单,类类源源码如下:
/
*** Returns the absolute value of an { @code int} value.
* If the argument is 源码-10的源码not negative, the argument is returned.
* If the argument is negative, the negation of the argument is returned.
*
*
Note that if the argument is equal to the value of
* { @link Integer#MIN_VALUE}, the most negative representable
* { @code int} value, the result is that same value, which is
* negative.
*
* @param a the argument whose absolute value is to be determined
* @return the absolute value of the argument.
*/
public static int abs(int a) {
return (a 0) ? -a : a;
}
二、绝对值的类类源特性及其运用。
1、源码正数的类类源绝对值是其本身。
2、源码负数的类类源绝对值是其相反数。
3、源码零的类类源绝对值是其本身。
绝对值:自减函数配合绝对值,源码先降序再升序。类类源
int number = 6;
System.out.println(原值输出:);
while(number=-6){
number --;
System.out.print(number+ );
}
System.out.println(\n绝对值输出:);
number = 6;
while(number=-6){
number --;
System.out.print(Math.abs(number)+ );
}
输出结果:
原值输出:
5 4 3 2 1 0 -1 -2 -3 -4 -5 -6 -7
绝对值输出:
5 4 3 2 1 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
案例
背景:输出如下图案。
A
B A B
C B A B C
D C B A B C D
E D C B A B C D E
F E D C B A B C D E F
G F E D C B A B C D E F G
分析:
1、A为中心点
2、每一行,力软源码使用先降序,再升序
3、字母可以换算成整数,A = 。那么,每行首个输出字母为 A +行数。
4、每行左右对称,每行输出字母数 = 行数*2 +1(字母A);
实现:
1、网站社区系统源码实现分析中的1~3步。以‘A’为中心点,先降序,再升序输出每行图案。
//调用
print(5);
/
*** 先降序,再升序 实现
* @param row
*/
private static void print(int row){
for(int i=0;i2*row+1;i++){
int printChar = A + Math.abs(row-i);
System.out.print(((char)printChar)+ );
}
}
输出如下:
F E D C B A B C D E F
2、步骤4中,每行输出字母数 = 行数*2 +1(字母A),那么:
每行应该显示的易语言 源码 位移字母除外的部分,打印空格。逻辑控制如下:
for(int j=0;j2*row+1;j++){
//逻辑输出字母。先降序、再升序逻辑输出的字母
int printChar = A + Math.abs(row-j);
//如果 [逻辑控制字母] 大于 [规定输出字母],则:
if(printCharfirstChar){
//输出空格
System.out.print( );
}else{
//输出字母
System.out.print(((char)printChar)+ );
}
}
3、完整代码:
//完整调用
printWithRow(7);
/
*** 先倒序 再正序 输出 英文大写字母
*
* @param row 行
*/
private static void printWithRow(int row){
for(int i=0;i
//规定输出字母。每行第一个显示出来的字母
int firstChar = A + i;
for(int j=0;j2*row+1;j++){
//逻辑输出字母。先降序、再升序逻辑输出的怎么导入src源码字母
int printChar = A + Math.abs(row-j);
//如果 [逻辑控制字母] 大于 [规定输出字母],则:
if(printCharfirstChar){
//输出空格
System.out.print( );
}else{
//输出字母
System.out.print(((char)printChar)+ );
}
}
//输出回车
System.out.println();
}
}
java中π怎么表示?用什么方法?
java中π用Math.PI表示,圆周率常量π被定义在java.lang.Math类中。输出:3.代码如下:
PI (π)的源码如下:
/
*** The { @code double} value that is closer than any other to
* <i>pi</i>, the ratio of the circumference of a circle to its
* diameter.
*/
public static final double PI = 3.;
扩展资料:
Java Math 类包含了用于执行基本数学运算的属性和方法,如初等指数、对数、平方根和三角函数。
Math 的方法都被定义为 static 形式,通过 Math 类可以在主函数中直接调用。
比较常见的还有一个底数e,在java Math中表示如下:
public static final double E = 2.;
参考资料:
Orcale官方API接口-Class Math
Java为ä»ä¹Math类建ç«ä¸äºå¯¹è±¡ï¼
æä¸ç¥éä½ ä»åªå¬è¯´mathæ¯staticç è³å°sunçæºä»£ç ä¸æ²¡æè¿ä¹å£°æ
public final class Math {
/
*** Don't let anyone instantiate this class.
*/
private Math() { }
Mathæ¯finalç±» ä¸æ¯staticç±»
è¿æ¯sunå ¬å¸å ³äºjava.lang.Mathç±»çå¼å¤´ï¼ç±äºæé å½æ°è¢«å£°æ为ç§æçï¼å°±æ¯è¯´æä¸è½è¢«å¤é¨è°ç¨ï¼æ以ä¸è½newåºæ¥ä¸ä¸ªæ°ç对象
Mathç±»çä½ç¨æ¯å¯¹æ°å¦è¿è¡ä¸äºæ©å ï¼è¿è¡ä¸äºå¸¸éå®ä¹ãæä½å®ä¹ï¼åªéè¦ä¼ å ¥åæ°å°±å¯ä»¥è¿åä½ éè¦çç»æï¼æ以大å¤æ¹æ³é½æ¯éææ¹æ³ç´æ¥ä½¿ç¨ï¼ä¸éè¦å®ä½ç±»å°±è¡
é£ä¸ªå£°æï¼Don't let anyone instantiate this class. ä¹è¯´æäº æè¿ä¸ªMath类就æ¯ä¸è®©ä½ åå§åä»»ä½å®ä¾ã Mathè¿å®ä¹ä¸ºfinalç±»ï¼ä¸å 许被继æ¿ã æ以永è¿ä¸ä¼åºç°Math对象
åææ¥äºä¸ä¸Mathçç¸å ³API æåç°æ说éäºä¸ä¸ªå°æ¹ï¼
Mathç±»çæææ¹æ³é½å®ç°éæåï¼ä¹å°±æ¯è¯´ï¼ææçæ¹æ³é½æ¯éææ¹æ³ 使ç¨Math.æ¹æ³åå°±å¯ä»¥ä½¿ç¨ ä¸æ¯é¨åï¼èæ¯å ¨é¨
用JAVA编写的科学计算器源代码
以下是一个简单的用Java编写的科学计算器的源代码示例:
java
import java.util.Scanner;
public class ScientificCalculator {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Welcome to the Scientific Calculator!");
System.out.println("Enter 'add', 'subtract', 'multiply', 'divide', 'sin', 'cos', 'tan', 'log', 'exp', 'sqrt', or 'quit' to exit.");
while (true) {
System.out.print("Enter operation (e.g., add 2 3): ");
String operation = scanner.nextLine();
if (operation.equalsIgnoreCase("quit")) {
break;
}
String[] parts = operation.split(" ");
double num1 = Double.parseDouble(parts[1]);
double num2 = Double.parseDouble(parts[2]);
switch (parts[0].toLowerCase()) {
case "add":
System.out.println(num1 + " + " + num2 + " = " + (num1 + num2));
break;
case "subtract":
System.out.println(num1 + " - " + num2 + " = " + (num1 - num2));
break;
case "multiply":
System.out.println(num1 + " * " + num2 + " = " + (num1 * num2));
break;
case "divide":
if (num2 != 0) {
System.out.println(num1 + " / " + num2 + " = " + (num1 / num2));
} else {
System.out.println("Error: Division by zero is not allowed.");
}
break;
case "sin":
System.out.println("sin(" + num1 + ") = " + Math.sin(Math.toRadians(num1)));
break;
case "cos":
System.out.println("cos(" + num1 + ") = " + Math.cos(Math.toRadians(num1)));
break;
case "tan":
System.out.println("tan(" + num1 + ") = " + Math.tan(Math.toRadians(num1)));
break;
case "log":
System.out.println("log(" + num1 + ") = " + Math.log(num1));
break;
case "exp":
System.out.println("exp(" + num1 + ") = " + Math.exp(num1));
break;
case "sqrt":
if (num1 >= 0) {
System.out.println("sqrt(" + num1 + ") = " + Math.sqrt(num1));
} else {
System.out.println("Error: Cannot calculate the square root of a negative number.");
}
break;
default:
System.out.println("Error: Invalid operation.");
break;
}
}
scanner.close();
System.out.println("Goodbye!");
}
}
这个科学计算器支持基本的四则运算(加、减、乘、除)以及一些科学运算(正弦、余弦、正切、对数、指数和平方根)。用户可以通过输入相应的操作和两个数字来执行计算。例如,输入“add 2 3”将计算2加3的结果。
代码首先导入了`Scanner`类,用于从用户处获取输入。然后,在`main`方法中,创建了一个`Scanner`对象,用于读取用户的输入。程序通过一个无限循环来持续接收用户的输入,直到用户输入“quit”为止。
在循环中,程序首先提示用户输入一个操作,然后读取用户的输入并将其分割为多个部分。接着,程序将第二个和第三个部分转换为`double`类型的数字,并根据第一个部分(即操作)执行相应的计算。
程序使用`switch`语句来根据用户输入的操作执行相应的计算。对于基本的四则运算,程序直接执行相应的计算并输出结果。对于科学运算,程序使用了Java的`Math`类中的相应方法。例如,对于正弦运算,程序使用了`Math.sin`方法,并将角度转换为弧度作为参数传递给它。
如果用户输入了无效的操作或无效