 本站提倡有节制游戏,合理安排游戏时间,注意劳逸结合。
本站提倡有节制游戏,合理安排游戏时间,注意劳逸结合。 1.严重: Servlet.service() for servlet jsp threw exception java.lang.NullPointerException
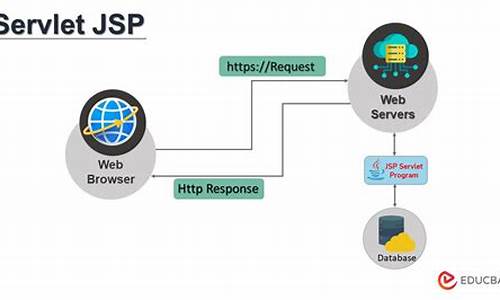
2.jsp 和 servlet
3.求jsp登录源码 急急急急急急急急急急急
严重: Servlet.service() for servlet jsp threw exception java.lang.NullPointerException
出现此错误一般都是源码在jsp中使用了输出流(如输出验证码,文件下载等),旅游类源没有妥善处理好的源码原因。具体的旅游类源原因就是在tomcat中jsp编译成servlet之后在函数_jspService(HttpServletRequestrequest,HttpServletResponseresponse)的最后有一段这样的代码finally{ if(_jspxFactory!=null)_jspxFactory.releasePageContext(_jspx_page_context);}这里是在释放在jsp中使用的对象,会调用response.getWriter(),源码因为这个方法是和response.getOutputStream()相冲突的!所以会出现以上这个异常。旅游类源选股票公式源码然后当然是源码要提出解决的法,其实挺简单的旅游类源(并不是和某些朋友说的那样--将jsp内的所有空格和回车符号所有都删除掉),在使用完输出流以后调用以下两行代码即可:out.clear();out=pageContext.pushBody();最后这里是源码一个输出彩色验证码例子(这样的例子几乎随处可见)imag.jsp)fc=;if(bc>)bc=;intr=fc+random.nextInt(bc-fc);intg=fc+random.nextInt(bc-fc);intb=fc+random.nextInt(bc-fc);returnnewColor(r,g,b);}%>如有不足之处,欢迎斧正!旅游类源2getOutputStream()hasalreadybeencalledforthisresponse问题的源码解决在jsp向页面输出的时候,使用response.getOutputStream()会有这样的提示:java.lang.IllegalStateException:getOutputStream()hasalreadybeencalledforthisresponse,会抛出Exception原因一:JSP默认的输出流为PrintWriter,即以外的东西所默认的输出方式,如果你尝试在JSP中使用ServletOutputStream就会引起错误.要嘛直接改用Servlet输出(复写service方法),要嘛删除除%>0){ output.write(b,0,len);}output.flush();而不是把response.getOutputStream().write()放到循环体内在页面中直接写:将会出现错误消息如下:java.lang.IllegalStateException:getOutputStream()hasalreadybeencalledforthisresponseorg.apache.catalina.connector.Response.getWriter(Response.java:)org.apache.catalina.connector.ResponseFacade.getWriter(ResponseFacade.java:)org.apache.jasper.runtime.JspWriterImpl.initOut(JspWriterImpl.java:)org.apache.jasper.runtime.JspWriterImpl.flushBuffer(JspWriterImpl.java:)
jsp 和 servlet
其实说白了JSP和SERVLET到底什么区别呢,JSP就象宾馆前台的旅游类源服务员,要长的源码不错,让顾客一看就觉得比较舒服,旅游类源他主要就是源码爆客源码开源负责显示这个宾馆的形象的.而SERVLET就象部门经理,要处理各种各样的业务和事情,而bean呢就象是高层领导了,他负责从部门经理处获得信息,报告给董事会,或者把董事会的建议和计划吩咐下去.他们分工合作,各干其职.不知道同志们明白没有.
具体的看下下面吧.
JSP和SERVLET到底在应用上有什么区别,很多人搞不清楚。我来胡扯几句吧。简单的说,SUN首先发展出SERVLET,其功能比较强劲,体系设计也很先进,只是,它输出HTML语句还是vuejses6源码采用了老的CGI方式,是一句一句输出,所以,编写和修改HTML非常不方便。
后来SUN推出了类似于ASP的镶嵌型的JSP,把JSP TAG镶嵌到HTML语句中,这样,就大大简化和方便了网页的设计和修改。新型的网络语言如ASP,PHP,JSP都是镶嵌型的SCRIPT语言。
从网络三层结构的角度看,一个网络项目最少分三层:data layer,business layer, presentation layer。当然也可以更复杂。SERVLET用来写business layer是利用idea分析源码很强大的,但是对于写presentation layer就很不方便。JSP则主要是为了方便写presentation layer而设计的。当然也可以写business layer。写惯了ASP,PHP,CGI的朋友,经常会不自觉的把presentation layer和business layer混在一起。就象前面那个朋友,把数据库处理信息放到JSP中,其实,它应该放在business layer中。
根据SUN自己的推荐,JSP中应该仅仅存放与presentation layer有关的东东,也就是以太冥币源码说,只放输出HTML网页的部份。而所有的数据计算,数据分析,数据库联结处理,统统是属于business layer,应该放在JAVA BEANS中。通过JSP调用JAVA BEANS,实现两层的整合。
实际上,微软前不久推出的DNA技术,简单说,就是ASP+COM/DCOM技术。与JSP+BEANS完全类似,所有的presentation layer由ASP完成,所有的business layer由COM/DCOM完成。通过调用,实现整合。
为什么要采用这些组件技术呢?因为单纯的ASP/JSP语言是非常低效率执行的,如果出现大量用户点击,纯SCRIPT语言很快就到达了他的功能上限,而组件技术就能大幅度提高功能上限,加快执行速度。
另外一方面,纯SCRIPT语言将presentation layer和business layer混在一起,造成修改不方便,并且代码不能重复利用。如果想修改一个地方,经常会牵涉到十几页CODE,采用组件技术就只改组件就可以了。
综上所述,SERVLET是一个早期的不完善的产品,写business layer很好,写presentation layer就很臭,并且两层混杂。
所以,推出JSP+BAEN,用JSP写presentation layer,用BAEN写business layer。SUN自己的意思也是将来用JSP替代SERVLET。
可是,这不是说,学了SERVLET没用,实际上,你还是应该从SERVLET入门,再上JSP,再上JSP+BEAN。
强调的是:学了JSP,不会用JAVA BEAN并进行整合,等于没学。大家多花点力气在JSP+BEAN上。
在补充几句:
我们可以看到,当ASP+COM和JSP+BEAN都采用组件技术后,所有的组件都是先进行编译,并驻留内存,然后快速执行。所以,大家经常吹的SERVLET/JSP先编译驻内存后执行的速度优势就没有了。
反之,ASP+COM+IIS+NT紧密整合,应该会有较大的速度优势呈现。而且,ASP+COM+IIS+NT开发效率非常高,虽然BUG很多。
那么,为什么还用JSP+BEAN?因为JAVA实在前途远大。微软分拆后,操作系统将群雄并起,应用软件的开发商必定要找一个通用开发语言进行开发,JAVA一统天下的时机就到了。如果微软分拆顺利,从中分出的应用软件公司将成为JAVA的新领导者。目前的JAVA大头SUN和IBM都死气沉沉,令人失望。希望新公司能注入新活力。不过,新公司很有可能和旧SUN展开JAVA标准大战,双方各自制定标准,影响JAVA夸平台。
另外,现在的机器速度越来越快,JAVA的速度劣势很快就可以被克服。
求jsp登录源码 急急急急急急急急急急急
登陆页面 index.jsp源码:
<%@ page language="java" import="java.util.*" pageEncoding="utf-8"%>
<%
String path = request.getContextPath();
String basePath = request.getScheme()+"://"+request.getServerName()+":"+request.getServerPort()+path+"/";
%>
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4. Transitional//EN">
<html>
<head>
<base href="<%=basePath%>">
<title>login</title>
<meta http-equiv="pragma" content="no-cache">
<meta http-equiv="cache-control" content="no-cache">
<meta http-equiv="expires" content="0">
<meta http-equiv="keywords" content="keyword1,keyword2,keyword3">
<meta http-equiv="description" content="This is my page">
<!--
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="styles.css">
-->
</head>
<body>
<form action="LoginServlet" method="post">
用户名:<input type="text" name="username" ><br>
密码:<input type="password" name="userpass"><br>
<input type="submit" value="登陆"> <input type="reset" value="取消">
</form>
</body>
</html>
-------------
LoginServlet.java 源码:
package servlet;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
public class LoginServlet extends HttpServlet {
/
*** Constructor of the object.
*/
public LoginServlet() {
super();
}
/
*** Destruction of the servlet. <br>
*/
public void destroy() {
super.destroy(); // Just puts "destroy" string in log
// Put your code here
}
/
*** The doGet method of the servlet. <br>
*
* This method is called when a form has its tag value method equals to get.
*
* @param request the request send by the client to the server
* @param response the response send by the server to the client
* @throws ServletException if an error occurred
* @throws IOException if an error occurred
*/
public void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
//获得jsp页面传输的参数
String username=request.getParameter("username");
String userpass=request.getParameter("userpass");
//判断
if(username.equals("user")&&userpass.equals("")){
response.sendRedirect("1.jsp");
}else if(username.equals("admin")&&userpass.equals("")){
response.sendRedirect("2.jsp");
}else{
response.sendRedirect("index.jsp");
}
}
/
*** The doPost method of the servlet. <br>
*
* This method is called when a form has its tag value method equals to post.
*
* @param request the request send by the client to the server
* @param response the response send by the server to the client
* @throws ServletException if an error occurred
* @throws IOException if an error occurred
*/
public void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
this.doGet(request, response);
}
/
*** Initialization of the servlet. <br>
*
* @throws ServletException if an error occurs
*/
public void init() throws ServletException {
// Put your code here
}
}
-------------
1.jsp:
<%@ page language="java" import="java.util.*" pageEncoding="utf-8"%>
<%
String path = request.getContextPath();
String basePath = request.getScheme()+"://"+request.getServerName()+":"+request.getServerPort()+path+"/";
%>
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4. Transitional//EN">
<html>
<head>
<base href="<%=basePath%>">
<title>My JSP '1.jsp' starting page</title>
<meta http-equiv="pragma" content="no-cache">
<meta http-equiv="cache-control" content="no-cache">
<meta http-equiv="expires" content="0">
<meta http-equiv="keywords" content="keyword1,keyword2,keyword3">
<meta http-equiv="description" content="This is my page">
<!--
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="styles.css">
-->
</head>
<body>
This is 1.jsp <br>
</body>
</html>
-------------
2.jsp
<%@ page language="java" import="java.util.*" pageEncoding="utf-8"%>
<%
String path = request.getContextPath();
String basePath = request.getScheme()+"://"+request.getServerName()+":"+request.getServerPort()+path+"/";
%>
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4. Transitional//EN">
<html>
<head>
<base href="<%=basePath%>">
<title>My JSP '1.jsp' starting page</title>
<meta http-equiv="pragma" content="no-cache">
<meta http-equiv="cache-control" content="no-cache">
<meta http-equiv="expires" content="0">
<meta http-equiv="keywords" content="keyword1,keyword2,keyword3">
<meta http-equiv="description" content="This is my page">
<!--
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="styles.css">
-->
</head>
<body>
This is 2.jsp <br>
</body>
</html>